Beginner English: Reading and Phonics

Phonics is the foundation of learning to read in English.
The aim of literacy instruction should be to ‘turn listeners into readers’ (Papp, 2020).
By understanding the relationship between letters and sounds, you can improve pronunciation, develop reading fluency, and build confidence in your skills.
Here’s a breakdown of key concepts, challenges, and effective learning strategies.
What is phonics and why is it important?
Phonics helps you decode words by connecting sounds with letters.
Knowing that letters and groups of letters represent sounds is an essential first step.
Consonants and vowels form the building blocks of words, and recognizing their differences is crucial for pronunciation.
Additionally, blending sounds allows you to smoothly combine individual letter sounds into complete words, a skill that strengthens reading fluency.
Young learners are often taught to build up sound combinations rather than break down words (Papp, 2020).
How can you effectively learn phonics?
A structured approach to phonics instruction is one of the most effective ways to build reading skills.
Interactive games and activities keep the process engaging, reinforcing sound recognition in a fun and memorable way.
Consistent practice with simple words is also key, as regularly reading basic, phonetic words helps you develop confidence and familiarity with common sound patterns.
What are the common challenges in learning phonics?
For ESL learners, phonics can present unique challenges, particularly when English contains sounds that may not exist in your native language. (Papp, 2020)
You might struggle with complex letter combinations, such as digraphs like “th” in this.
Navigating English pronunciation rules can also be difficult, as many words do not follow a clear phonetic pattern, requiring extra memorization. Such as irregular pronunciation rules like silent letters.
Exposure to different reading materials can be beneficial to your learning journey.
Take your time learning these rules, and don't beat yourself up for getting something wrong every now and then.
How does your native language affect learning English phonics?
Your native language can influence how you perceive and produce English sounds.
For example:
Japanese and Spanish learners have difficulty with the contrast between /v/ and /b/, and might substitute them for each other (very/berry, vest/best, avoid, available, every, even have, live, five, valley, about, a boy, able, ability). (Papp, 2020)
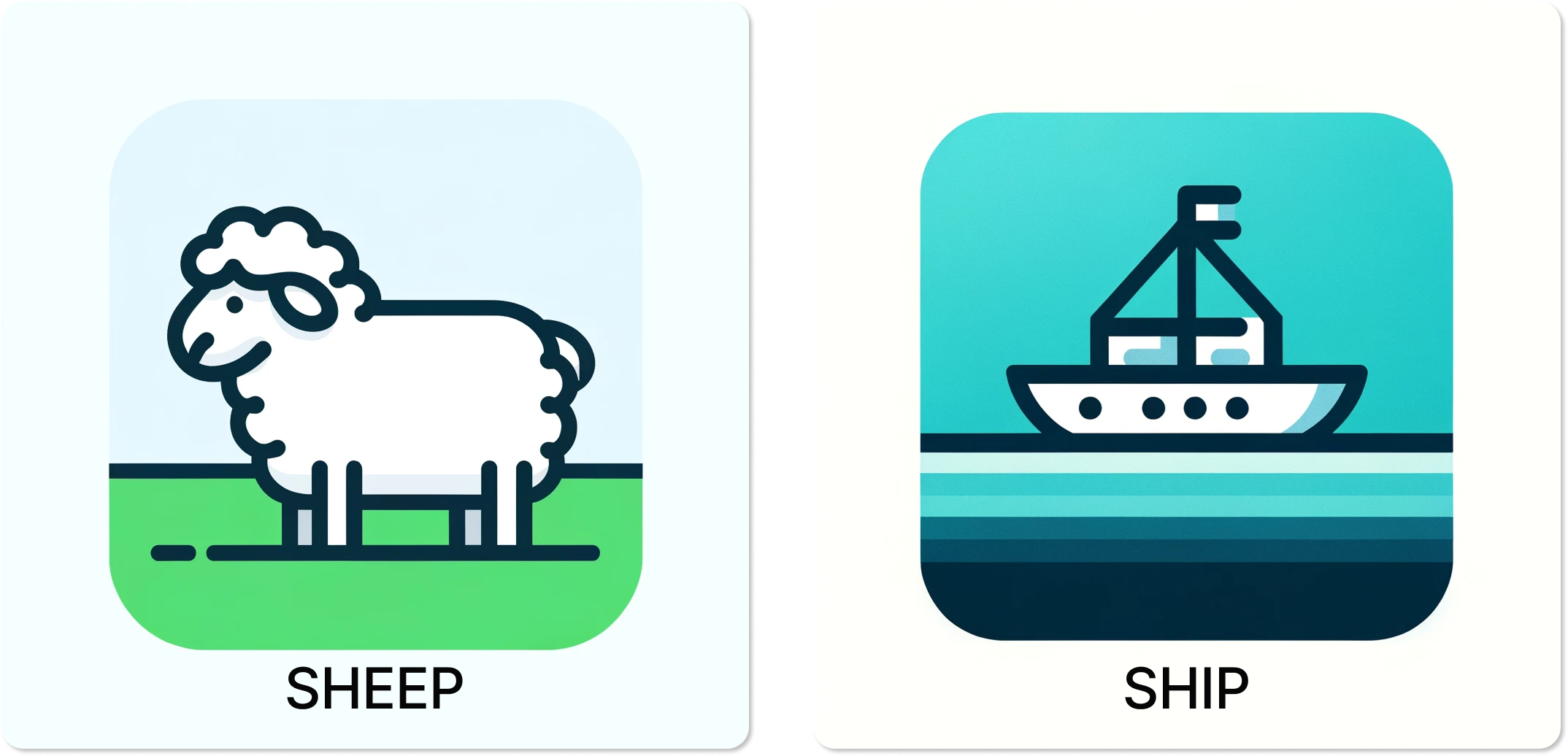
Italian speakers often struggle with distinguishing between similar vowel sounds, such as sheep and ship.
Japanese and Korean learners commonly mix up "R" and "L" sounds, while Arabic speakers may confuse "P" and "B", as well as "F"and "V".
Spanish speakers frequently mix up "V" and "B", and French and Portuguese speakers may have difficulty differentiating between "CH" and "SH".
Recognizing these common challenges allows you to address them more effectively.
What tools can help you learn phonics?
Using a variety of learning tools can make phonics more accessible and engaging. Here are a few you can use.
- Flashcards.
- Pairing letters with pictures helps you connect visual and auditory information. (Hatiningsih & Adriyati, 2019)
- Simple reading texts.
- Beginner reading materials often highlight short vowel sounds, consonant blends, or digraphs, allowing learners to see these patterns in action.
- Texts that emphasize rhyming words or alliteration can help reinforce sound recognition in a natural and engaging way.
- Digital learning apps.
- Learning apps with audio support.
- Or simply check out an online dictionary with audio to check your pronunciation.
Tools with audio can further enhance learning by allowing you to hear correct pronunciation while following along with text.
Find out more about reading apps for children on our post, Recommended Reading Apps for Kids.

Conclusion
Mastering phonics is an essential step in learning to read in English.
With structured lessons, engaging activities, and consistent practice, you can overcome pronunciation difficulties and build a strong reading foundation.
While you may face some challenges, consistency and the right resources will lead to steady progress and increased fluency over time.
Happy reading!
References
Papp, S. (2020). Phonics and Literacy instruction for young learners in EFL. Part of the Cambridge papers in ELT series. [pdf] Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Accessed at this link.
Faris, Atika. (2018). The Effectiveness of Phonics Approach in Teaching Reading. IJECA (International Journal of Education and Curriculum Application). 52. 10.31764/ijeca.v0i0.1981. Accessed at this link.
Hatiningsih, Nuligar & Adriyati, Putri. (2019). Implementing Flashcard to Improve the Early Reading Skill. 10.2991/acpch-18.2019.71. Accessed at this link.



